In the era of rapid technological advancement, the fusion of Internet of Things (IoT) and Big Data has emerged as a pivotal strategy for businesses seeking to elevate operational efficiency and innovate their service offerings.
How is Big Data used in various industries?
Big Data, characterized by its volume, velocity, and variety, plays a crucial role across multiple sectors:
- Healthcare: Leveraging patient data from various sources, including wearables and electronic health records, to improve treatment outcomes and predict patient trends.
- Retail: Analyzing customer behavior and preferences to optimize product placements and personalize marketing efforts.
- Manufacturing: Monitoring equipment and production lines to predict failures and optimize maintenance schedules.
- Transportation: Utilizing data from sensors and GPS systems to enhance logistics and reduce operational costs.
- Energy: Managing grid operations and forecasting energy consumption patterns to increase efficiency and support sustainable practices.
By examining these implementations, businesses can glean how Big Data adapates to distinct industry needs, promoting a data-driven approach to problem-solving.
How do IoT and Big Data relate to each other?
IoT and Big Data are intrinsically linked, with IoT devices generating a massive influx of real-time data that Big Data technologies store, process, and analyze. This relationship enables:
- Enhanced Data Collection: IoT devices provide continuous, real-time data streams that feed Big Data systems.
- Advanced Data Analytics: Big Data tools analyze this information, deriving insights that can improve decision-making and operational efficiency.
- Actionable Intelligence: The integration facilitates proactive actions based on data-driven insights, significantly benefiting business operations.
How Big Data is used in IoT?
Data Aggregation
In the realm of IoT, data aggregation involves collecting and consolidating data from a variety of IoT devices, sensors, and systems. This process not only captures a vast array of data points but also converts them into a more manageable form that can be effectively analyzed.
For example, a smart city initiative may involve thousands of sensors spread across different locations—traffic lights, pollution monitors, and public transport vehicles—all providing real-time data. Aggregating this data helps city planners obtain a holistic view of urban dynamics, such as peak traffic times, areas of high pollution, and the efficiency of public transportation. By doing so, they can identify critical issues like traffic congestion and air quality levels, facilitating timely interventions.
Data Processing and Analysis
Once data is aggregated, the next step involves processing and analyzing this information using advanced algorithms and machine learning models. This phase is critical as it turns raw data into actionable insights. For instance, in the retail sector, IoT devices track customer movements and interactions within a store.
Big Data technologies process this vast amount of data to reveal patterns, such as popular paths through the store and dwell times at specific displays, which can be critical for optimizing store layouts and improving sales strategies. Additionally, predictive analytics can forecast future buying trends, helping retailers stock products more efficiently and tailor promotions to customer preferences.
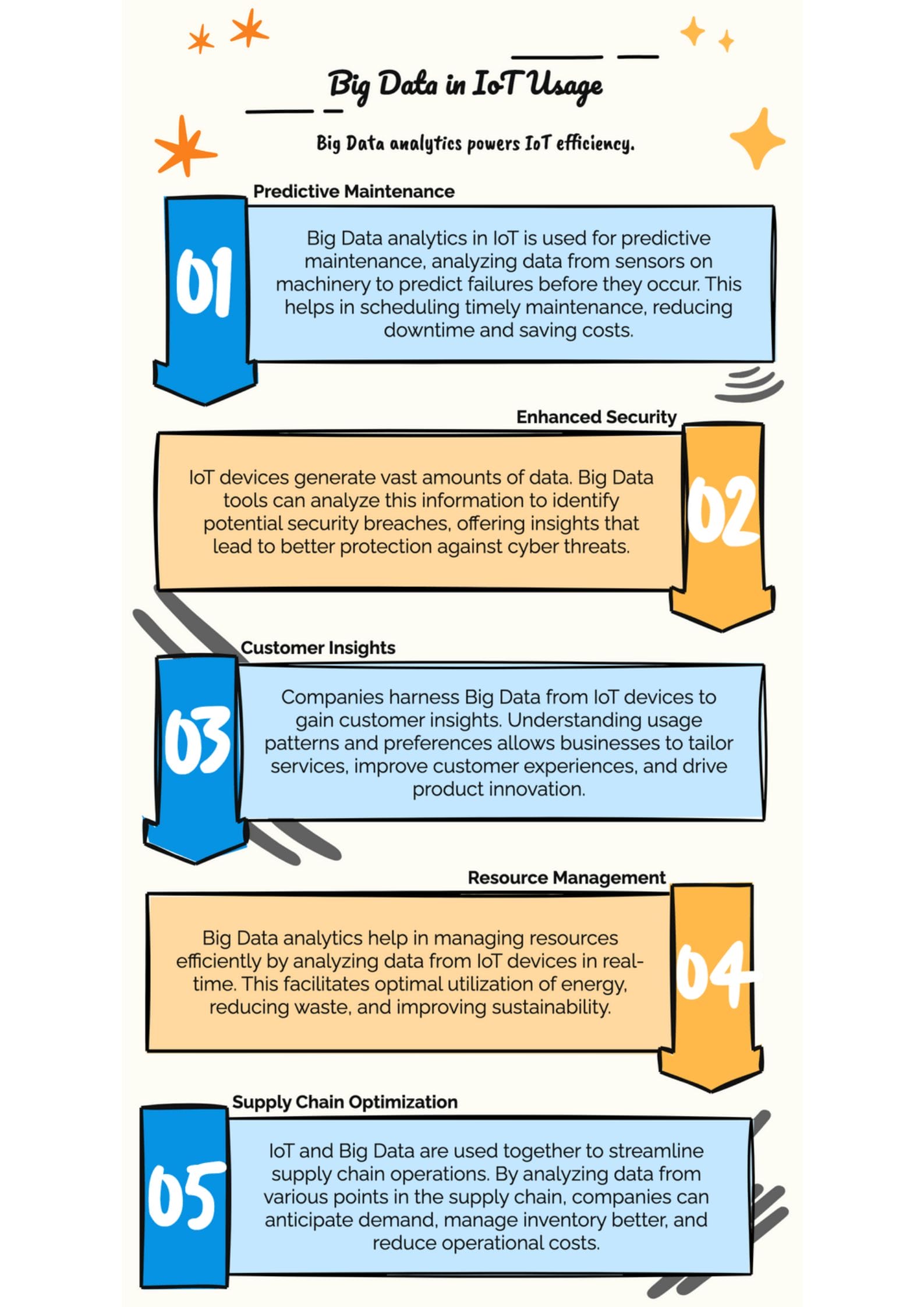
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is a prime example of how IoT and Big Data can revolutionize industry practices. By analyzing data from machinery sensors, algorithms can predict when a piece of equipment is likely to fail. For example, in the manufacturing industry, sensors on a production line machine monitor various parameters such as temperature, vibration, and sound.
By analyzing historical and real-time data, the system can identify patterns that precede equipment failures. This preemptive insight allows companies to perform maintenance only when necessary, thereby reducing downtime and maintenance costs, and extending the life of the equipment.
Optimization of Operations
Real-time data analysis is key to optimizing operations across various sectors. In logistics, for instance, IoT devices track vehicle locations, fuel usage, and cargo conditions. By analyzing this data in real time, logistic companies can optimize routes to reduce fuel consumption and delivery times, adjust loads to maximize capacity utilization, and improve overall operational efficiency.
This not only reduces operational costs but also enhances service delivery by ensuring goods are transported efficiently and safely.
Personalization and Customization
Big Data facilitates the personalization and customization of services and products by analyzing data collected from IoT devices. In the smart home sector, IoT devices such as thermostats, lighting systems, and security cameras collect data on user preferences and behaviors.
Big Data algorithms analyze this data to customize the home environment according to the residents’ preferences, adjusting lighting, temperature, and even suggesting security settings based on historical usage patterns. This level of customization not only enhances user satisfaction but also increases energy efficiency by adapting the home’s functionalities to suit actual usage.
Improved Decision-making
With the aid of comprehensive analytics, businesses are empowered to make quick, informed decisions. For example, IoT sensors across a power grid can monitor electricity consumption in real time. Big Data analytics can process this data instantly to detect anomalies or surges in demand.
Utility companies can use this information to make immediate decisions on energy distribution, potentially preventing outages and promoting stable energy supply across regions.
Security and Risk Management
In an IoT-enabled environment, security and risk management are crucial. Big Data analytics play a pivotal role in enhancing security by continuously analyzing data from IoT devices for unusual patterns that may indicate potential security threats.
For instance, in financial services, IoT devices connected to a network can be monitored for unusual data access or transfers that could signify a cybersecurity breach. By detecting these anomalies early, financial institutions can act swiftly to mitigate risks and protect sensitive data.
Scalability and Flexibility
As IoT deployments expand, Big Data solutions offer the scalability and flexibility needed to manage increasing data volumes. For example, in agriculture, as more IoT devices such as soil sensors and drones are used, the amount of data collected grows exponentially.
Big Data systems scale to accommodate this growth, enabling farmers to continue gaining insights into soil conditions, crop health, and environmental factors without performance degradation, thus supporting efficient farm management and increased agricultural productivity.
Types of analytics you can use in your IoT
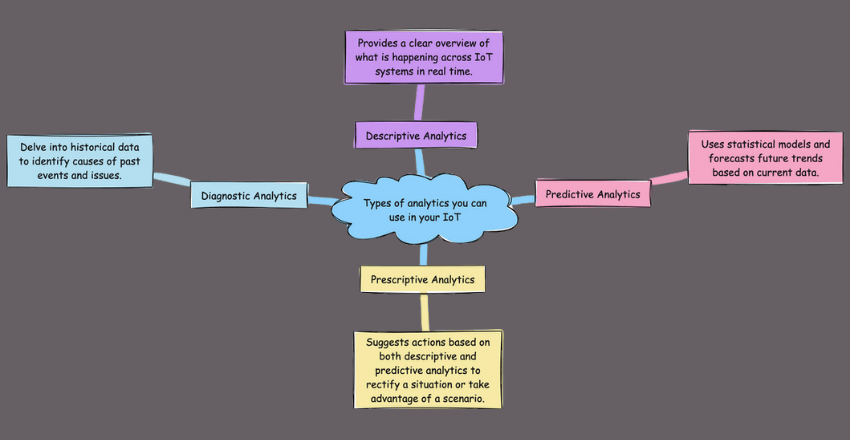
- Descriptive Analytics: Provides a clear overview of what is happening across IoT systems in real time.
- Predictive Analytics: Uses statistical models and forecasts future trends based on current data.
- Prescriptive Analytics: Suggests actions based on both descriptive and predictive analytics to rectify a situation or take advantage of a scenario.
- Diagnostic Analytics: Delve into historical data to identify causes of past events and issues.
Future of IoT and Big Data in the business
The convergence of IoT and Big Data is set to redefine industry landscapes by enabling more connected, intelligent, and autonomous systems. As machine learning and AI evolve, the integration of these technologies with Big Data will likely lead to even more profound transformations in how businesses operate and compete.
External Source
FAQs
What are the benefits of integrating Big Data with IoT? Integrating Big Data with IoT helps in enhancing operational efficiency, improving customer experience, reducing costs through predictive maintenance, and making informed decisions through advanced data analytics.
How can Big Data improve decision-making in IoT? Big Data analytics can process vast amounts of IoT-generated data in real-time, providing businesses with actionable insights that lead to informed decision-making and proactive management.
What should businesses consider when implementing Big Data in IoT? Businesses should consider data privacy and security, the scalability of the Big Data solutions, and the
integration capabilities with existing IoT frameworks to ensure a seamless and effective implementation.